Foundries in India
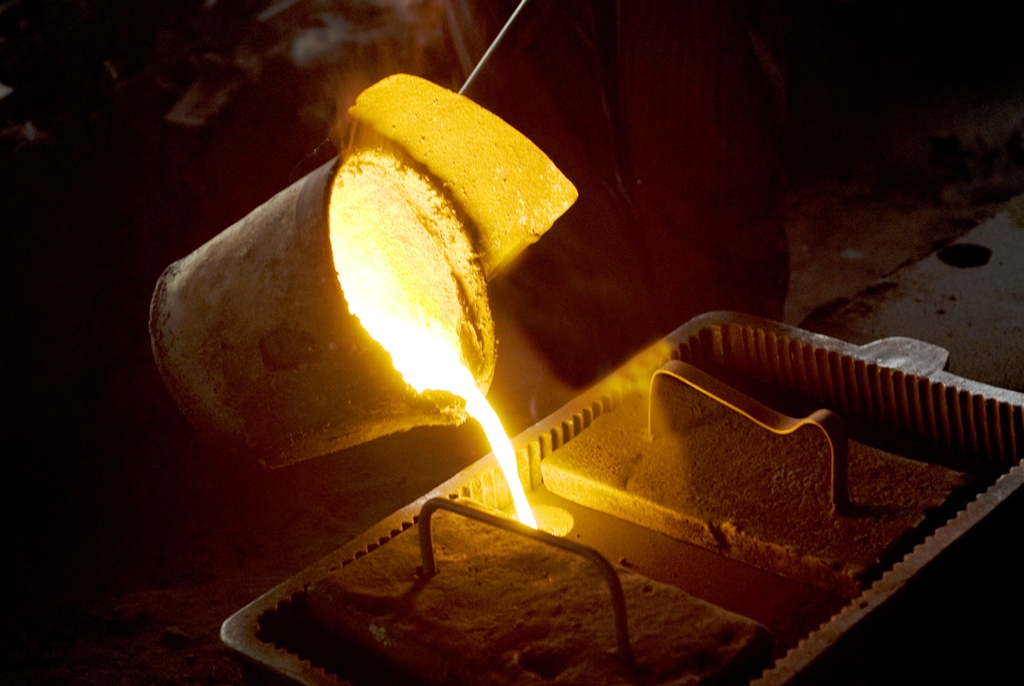

Foundries are factories or workshops which cast molten metal into a mould. This can be done manually (static casting) or through automation using injection die or continuous casting processes.
Typically, this process would involve the following steps:
- Preparation of a mould casting
- Melting and pouring of metal into the mould
- Removal of the casting
- Finishing of the casting
Iron and steel castings are produced at ferrous foundries and castings of copper-based alloys, aluminium-based alloys and other alloys are produced at non-ferrous foundries.
To melt the metal, specialised furnaces are used. The commonly used furnace types include electric arc furnaces (EAF), induction furnaces, cupolas for ferrous foundries while for producing aluminium, bronze, and brass castings, reverberatory and crucible furnaces are used.
Metal cast components produced at the various foundries and made of ferrous, non ferrous, Aluminium alloy, graded cast iron, ductile Iron and Steel, find their applications in various sectors like Automobiles, Railways, Machine Tools, Defence, Earth Moving /Textile/Cement/Electrical/Power Machinery, Pumps Compressors /Valves, Aero & Sanitary Pipes & Fittings.
The Foundry Industry in India
With an output of 9.344 Million MT of castings, the Foundry Industry in India has a turnover of approximately USD 15 billion, with exports totalling approximately USD 2 billion. Grey iron castings account for the major share of approximately 68% of the total castings produced.
In India, there are around 4500 units/foundries. 85% of these can be classified as Small Scale Units, 10% as Medium & 5% as Large Scale Units. Almost about 800 of these units have International Quality Accreditation. A number of large foundries are modern and globally competitive, and are working at almost full capacity. Most of these foundries have cupolas (type of furnace) using LAM (Low Ash Metallurgical) Coke. With growing awareness about environmental impact, many foundries are switching over to induction furnaces (eg. some units in Agra are changing over to cokeless cupolas).
The industry is labour intensive and directly employs about 5, 00,000 people. About 1, 50,000 people find their employment (indirectly) though related activities. The small scale units usually employ manual labour while the medium & large units are semi/ largely mechanized.
Foundry units can be categorized as small, medium, and large categories based on their annual production as follows:
- Small Units (annual production up to 1,000 tonnes)
- Medium Units (annual production 1,001 tonnes to 10,000 tonnes)
- Large Units (annual production more than 10,000 tonnes)
Locations of Foundries in India
Important foundry clusters in India can be found at these locations:
1. Punjab: Batala, Jalandar and Ludhiana
2. Delhi
3. Uttar Pradesh: Agra
4. Gujrat: Mainly Rajkot
5. West Bengal: Howrah
6. Maharastra: Mumbai, Kolhapur
7. Madhya Pradesh: Bhopal/Indore
8. Karnataka: Belgaum
9. Tamil Nadu: Chennai, Coimbatore
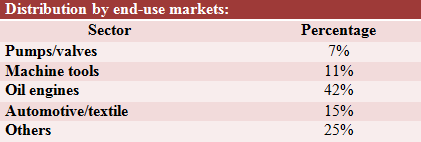
Overview of Distribution of Foundries Classified by End-Use Markets
To give a general indication as well as for brevity, I will be dealing with only a few of the prominent foundry clusters.
Belguam
Belgaum, Karnataka has over 100 foundry units spread out over Udyambag and Macche industrial areas. Here, the industry developed in response to the demand from the automobile industry at Pune, Maharastra. This particular industrial cluster is well known for high precision, high volume and economical castings, with almost 20% of the foundry units having ISO 9000 certification. Almost an equal number of them export these castings.
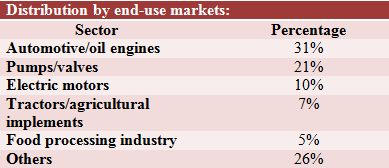
Coimbatore
Located in Tamil Nadu, this foundry cluster caters mainly to the needs of the local textile and pump-set industries. There are about 600 foundry units in Coimbatore, spread out over Thanneer Pandal/Peelamedu, Ganapathy, SIDCO, Singanallur, Mettupalayam Road and Arasur Village. About 10% of the foundry units export castings. Nearly 50% of foundry units are manufacturing castings for the pump-set industry.
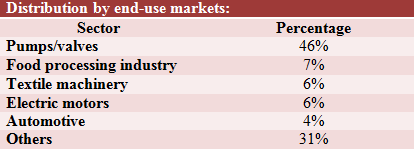
Batala and Jalandhar
The majority of the foundry units in Batala and Jalandhar, Punjab, are small-scale units which produce grey iron castings (machinery parts and agricultural implements). Of these, about 15% of them also export their products.
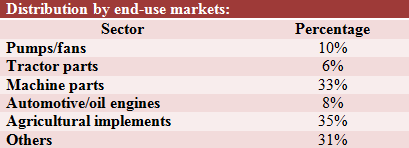
Kolhapur
Kolhapur, Maharashtra, mainly produces automotive castings. This cluster came up to cater to the casting requirements of the local industries like oil engine manufacturing, sugar mills and machine tool industry. There are about 250 foundry units, spread out over Kolhapur, Sangli, Ichalkaranji and Hatkanangale areas. About 25% of foundry units here are exporting castings.
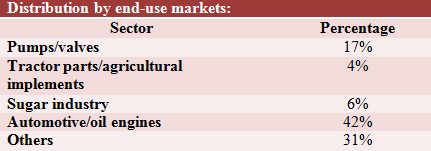
Rajkot
Rajkot , Gujarat has about 500 foundry units mainly catering to the casting requirements of the local diesel engine industry. It is spread out over Aji Vasahat, Gondal Road and Bhavanagar Road areas. Majority of the foundry units at Rajkot produces grey iron castings for the domestic market (about 10% of the foundry units are into exports of electric motor castings).
Industrial Outlook for 2015
The Indian foundry industry has an edge over China in producing complex machined and precision castings which meet international quality standards. Nearly USD $ 3 billion is required to support the growing domestic industry and export. The Government of India has reduced tariffs on imported capital goods. This has resulted in increasing the annual average amount of FDI. Now, FDI projects are permitted through an automatic approval process. Privatization of industry is being encouraged to enable foreign companies to invest or enter into joint ventures with Indian foundries.
Numerous international corporate houses from USA, EU and East-Asian Countries have increased their overseas foundry operations, by basing these activities in India. Examples include foundries of VOLVO in Chennai, of Suzuki in Haryana, and collaborations of Hyundai Motors with Delphi, and Sundaram Clayton with Cummins.
Contracts of foundry products (for export) worth $ 40 Million have been signed by Ford India, Tata-Cummins, and GM. Technology transfer through JV with foreign companies is being encouraged by the government. Under the industrial infrastructure upgradation scheme, the foundry clusters located in Belgaum, Coimbatore and Howrah are being modernized.
As of now, the developments in the Indian Foundry industry in terms of technical improvements, modernization, exports and FDI are turning up the heat!
Add a comment
0 Comments Add a Comment?